Features of ART Models
Definition
Adaptive Resonance Theory (ART) models are a class of neural networks designed to perform pattern recognition and clustering while addressing the stability-plasticity dilemma. They ensure that new information can be learned without erasing previously stored information, making them suitable for real-time and incremental learning tasks.
Key Concepts
- Stability-Plasticity Dilemma: The balance between retaining existing memories (stability) and learning new patterns (plasticity).
- Resonance: A process where the network successfully matches an input pattern with an existing memory, leading to learning or reinforcement.
- Vigilance Parameter: A threshold that determines the similarity required for resonance, controlling the granularity of pattern recognition.
- Fast and Slow Learning: Mechanisms to quickly adapt to new patterns or gradually refine existing patterns, respectively.
Detailed Explanation
Stability and Plasticity
- Stability: The ability of the network to retain learned patterns over time without significant degradation.
- Plasticity: The capacity of the network to learn new patterns and adjust its structure accordingly.
Resonance Mechanism
- Pattern Matching: The input vector is compared with the stored weight vectors to find the closest match.
- Vigilance Test: The degree of match is checked against the vigilance parameter. If it passes, resonance occurs, leading to learning.
- Reset Mechanism: If the match does not pass the vigilance test, the network resets and searches for another match, ensuring that new and significantly different patterns can be learned.
Vigilance Parameter
- High Vigilance: Requires close matches, leading to fine-grained clustering with many categories.
- Low Vigilance: Allows broader matches, resulting in fewer, more general categories.
Fast and Slow Learning
- Fast Learning: Immediate adjustments to the weights when a new pattern is learned, allowing quick adaptation.
- Slow Learning: Gradual refinement of weights over multiple presentations of the input, enhancing the stability of learned patterns.
Diagrams
Basic Structure of an ART Network
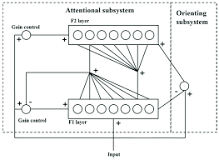
Resonance and Vigilance Mechanism

Links to Resources
- Adaptive Resonance Theory (ART) Overview: Detailed reference entry on ART networks, explaining their principles and applications.
- ART Network Tutorial: An accessible tutorial on ART networks with examples and practical insights.
- Neural Networks and Learning Machines by Simon Haykin: Textbook providing an in-depth discussion on ART networks and other neural network models.
Notes and Annotations
- Summary of Key Points:
- ART models address the stability-plasticity dilemma, enabling stable yet flexible learning.
- The vigilance parameter is key to controlling the specificity of pattern recognition.
- Fast and slow learning mechanisms allow ART models to adapt quickly to new patterns and refine existing ones gradually.
- Personal Annotations and Insights:
- ART models are ideal for environments requiring continuous learning and adaptation without the risk of catastrophic forgetting.
- The ability to adjust the vigilance parameter provides ART networks with significant flexibility in handling various types of data and noise levels.
Backlinks
- Unsupervised Learning Techniques: Refer to broader discussions on unsupervised learning methods to understand the context of ART models.
- Competitive Learning Networks: Connect to notes on competitive learning networks for a comparative perspective on different unsupervised learning strategies.
- Neural Network Models Overview: Link to an overview of various neural network models to see where ART networks fit in the landscape of machine learning techniques.