Solve given two player search tree using Alpha-beta pruning.
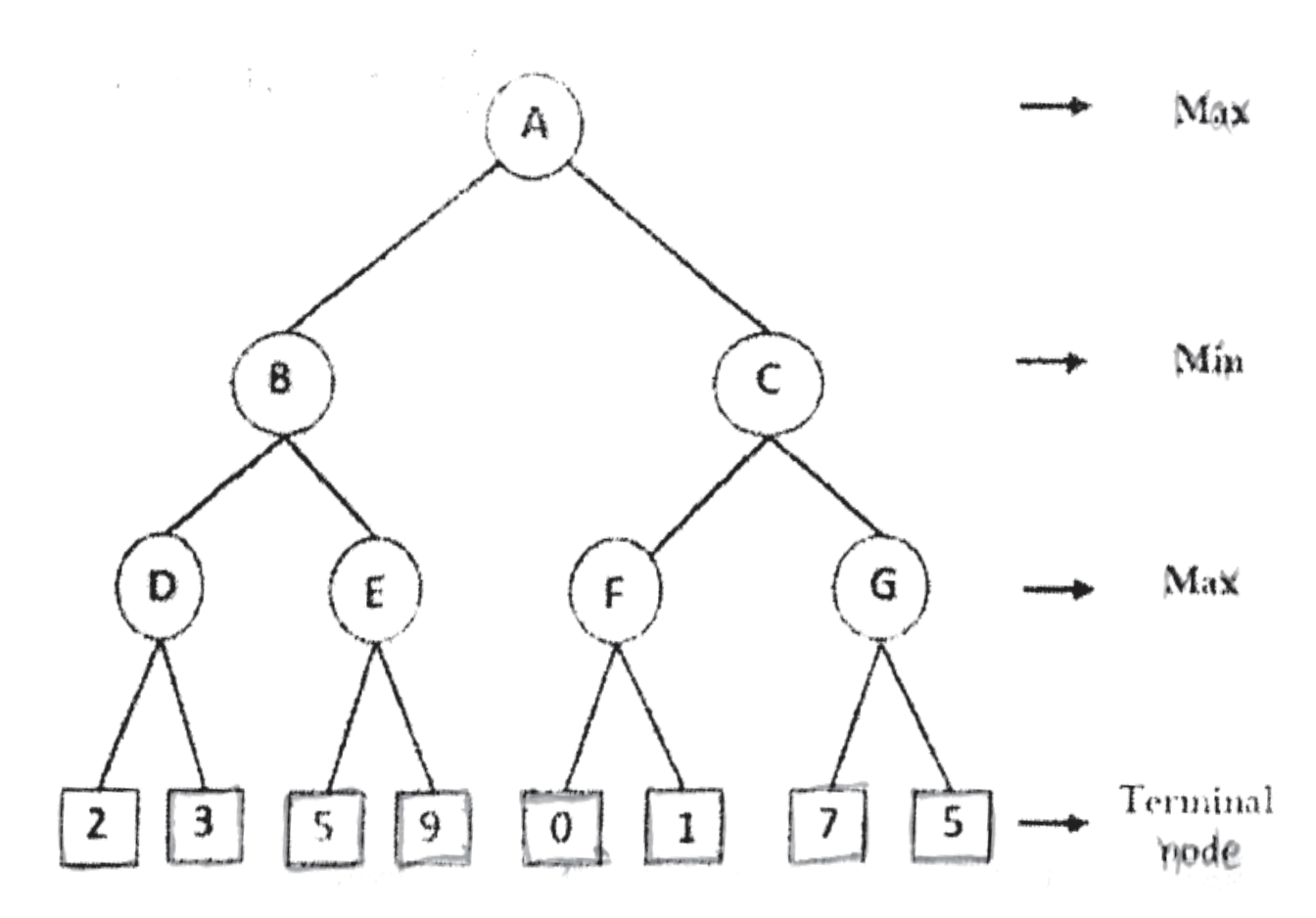
Step-by-Step Alpha-Beta Pruning
The given tree has three levels:
- Level 1 (root node): Max
- Level 2: Min
- Level 3: Max (leaf nodes with values)
We'll start with initial values of alpha as (-\infty) and beta as (+\infty).
-
Root Node A (Maximizer):
- Initialize (\alpha = -\infty)
- Initialize (\beta = +\infty)
-
Node B (Minimizer):
-
Explore child D:
- ( \alpha = -\infty, \beta = +\infty )
- Node D:
- Leaf values: 2 and 3
- (\max(2, 3) = 3)
- Value of D is 3
- Update (\beta) at B: (\beta = \min(\beta, 3) = 3)
-
Explore child E:
- ( \alpha = -\infty, \beta = 3 )
- Node E:
- Leaf values: 5 and 9
- (\max(5, 9) = 9)
- Value of E is 9
- Update (\beta) at B: (\beta = \min(\beta, 9) = 3) (unchanged)
- Prune branch E because ( \beta ) is already lower than the possible value of E's children.
-
Value of B is 3
-
Update (\alpha) at A: (\alpha = \max(\alpha, 3) = 3)
-
-
Node C (Minimizer):
-
Explore child F:
- ( \alpha = 3, \beta = +\infty )
- Node F:
- Leaf values: 0 and 1
- (\max(0, 1) = 1)
- Value of F is 1
- Update (\beta) at C: (\beta = \min(\beta, 1) = 1)
- Prune the remaining branches at C because (\beta \leq \alpha). Therefore, we do not need to explore G.
-
Value of C is 1
-
Update (\alpha) at A: (\alpha = \max(\alpha, 1) = 3) (unchanged)
-
Result
The value of the root node A (Max) is determined by comparing the values of B and C. Since we have pruned some branches, our evaluation suggests:
- Value of B is 3
- Value of C is 1
Thus, the optimal value for A (Max) is (\max(3, 1) = 3).
Pruned Tree
The pruned tree can be visualized as follows:
A (3)
/ \
B (3) C (1)
/ /
D (3) F (1)
/ \
(2) (3)
- Nodes E and G were pruned because their branches did not affect the final decision.
Conclusion
Using alpha-beta pruning, we reduced the number of nodes explored, improving efficiency while maintaining the correctness of the optimal decision. The optimal value for the root node A is 3.