Explain predictive, Descriptive, and Prescriptive data analysis. And also mention their difference.
Certainly! Let's dive deep into the three primary types of data analysis: predictive, descriptive, and prescriptive. Each type serves a distinct purpose in the data analysis lifecycle and offers unique insights.
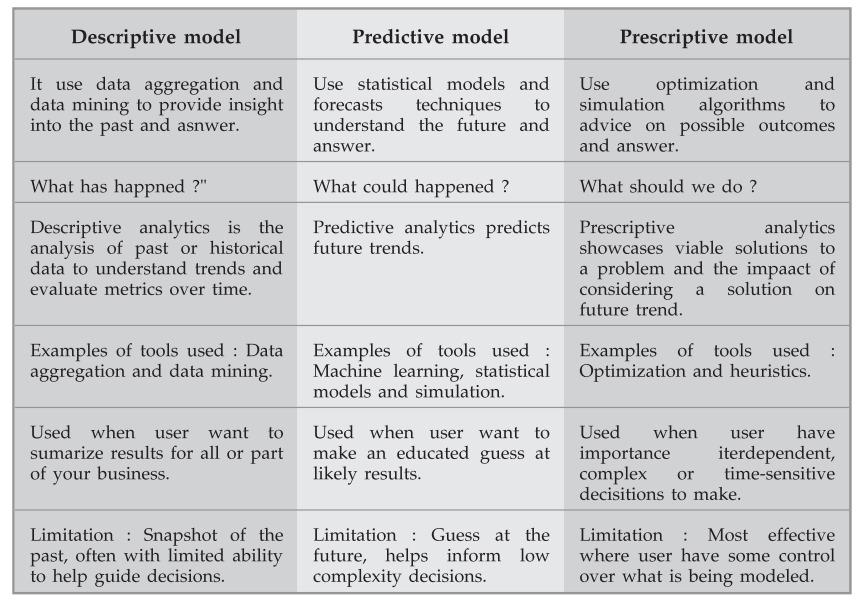
Predictive Data Analysis
Predictive data analysis is focused on forecasting future events based on historical data. It uses statistical models and machine learning techniques to predict outcomes by identifying patterns and relationships in the data.
Key Techniques:
- Regression Analysis: Predicts a continuous outcome variable based on one or more predictor variables.
- Linear Regression: Models the relationship between a dependent variable and one or more independent variables linearly.
- Logistic Regression: Used for binary classification tasks, modeling the probability of a binary outcome.
- Time Series Analysis: Analyzes data points collected or recorded at specific time intervals to forecast future values.
- Machine Learning Algorithms: Techniques like decision trees, random forests, support vector machines, and neural networks used to predict outcomes based on input data.
Examples:
- Predicting stock prices, sales forecasts, customer churn rates, and disease outbreaks.
Descriptive Data Analysis
Descriptive data analysis aims to summarize and interpret historical data to understand what has happened in the past. It provides a snapshot of past events and trends through aggregation and data mining techniques.
Key Techniques:
- Data Aggregation: Summarizing large datasets to provide an overview. This includes calculating means, medians, totals, and counts.
- Data Visualization: Creating charts, graphs, and dashboards to present data insights visually.
- Descriptive Statistics: Measures of central tendency (mean, median, mode) and measures of variability (range, variance, standard deviation).
Examples:
- Summarizing sales performance over the last quarter, visualizing customer demographics, and analyzing website traffic patterns.
Prescriptive Data Analysis
Prescriptive data analysis goes beyond predicting future outcomes to recommend actions that can influence desired results. It combines insights from predictive analysis with optimization and simulation techniques to suggest the best course of action.
Key Techniques:
- Optimization Models: Mathematical models that determine the best solution from a set of feasible options, often used in resource allocation, scheduling, and logistics.
- Simulation: Techniques like Monte Carlo simulation that model the probability of different outcomes in a process that cannot easily be predicted due to the intervention of random variables.
- Decision Analysis: Frameworks and methodologies for making decisions in the presence of uncertainty and multiple objectives.
Examples:
- Recommending inventory levels to minimize costs while meeting demand, suggesting marketing strategies to maximize customer engagement, and advising on financial portfolios to achieve optimal returns.
Differences Between Predictive, Descriptive, and Prescriptive Data Analysis
| Aspect | Descriptive Analysis | Predictive Analysis | Prescriptive Analysis |
|---|---|---|---|
| Objective | Understand and summarize past events | Forecast future events based on historical data | Recommend actions to achieve desired outcomes |
| Focus | What has happened? | What will happen? | What should we do? |
| Techniques | Data aggregation, visualization, descriptive statistics | Regression, time series analysis, machine learning algorithms | Optimization models, simulation, decision analysis |
| Output | Reports, dashboards, summaries | Predictive models, forecasts | Actionable recommendations, optimal strategies |
| Examples | Sales performance reports, customer demographics | Sales forecasts, customer churn prediction | Inventory optimization, marketing strategy recommendations |
| Time Orientation | Past | Future | Future with actionable insights |
| Complexity | Low to medium | Medium to high | High |
Practical Application in Data Science
In a real-world data science project, these three types of analysis often work together. For instance, a retail company might use:
- Descriptive analysis to understand past sales trends.
- Predictive analysis to forecast future sales.
- Prescriptive analysis to determine optimal inventory levels and marketing strategies.
Conclusion
Understanding and applying these three types of data analysis—descriptive, predictive, and prescriptive—enable organizations to not only gain insights from their data but also to forecast future events and make informed decisions that drive business success. Each type builds on the previous one, offering progressively deeper insights and actionable outcomes.
MM - Explain predictive, Descriptive, and Prescriptive data analysis. And also mention their difference.MM - Explain predictive, Descriptive, and Prescriptive data analysis. And also mention their difference.Creating mind maps with concise keywords and short sentences is an excellent way to recall the key concepts of predictive, descriptive, and prescriptive data analysis. Here are the essential keywords and short sentences for each type of analysis to help you create your mind maps: Descriptive Data Analysis Objective**: Summarize past events Focus**: What happened? Techniques**: * Data Aggregation: Summarize large datasets * Data Visualization: Charts, graphs, dashboards * Descriptive Stat