Components of the Data Analytical Architecture
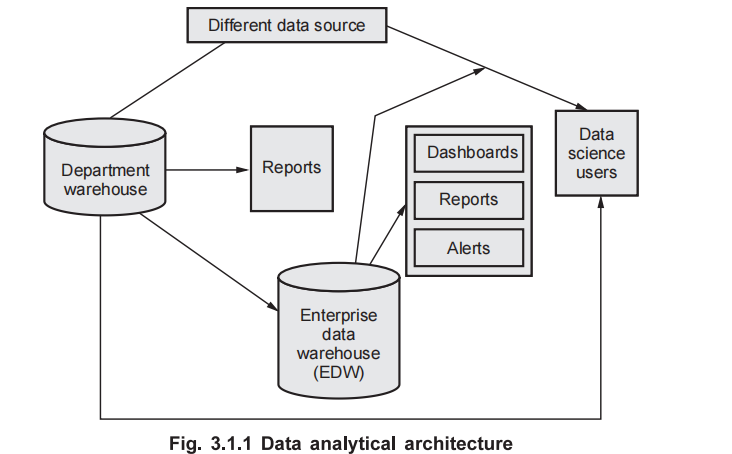
The diagram you provided illustrates a typical Data Analytical Architecture. Let's break down and explain each component and the flow of data within this architecture:
Components of the Data Analytical Architecture
-
Different Data Sources:
- This represents the various origins of data that can include databases, sensors, social media, and more.
- These sources provide raw data which needs to be collected and processed.
-
Department Warehouse:
- A storage solution specific to departmental needs, where data relevant to a particular department is stored.
- This enables department-specific analysis and reporting.
- Reports generated from this warehouse serve the department's unique requirements.
-
Enterprise Data Warehouse (EDW):
- This is a centralized repository that consolidates data from various departments and sources across the organization.
- EDW ensures that data is stored in an integrated manner, supporting a holistic view of the organization’s data.
-
Reports:
- These are generated insights derived from the data stored in the department warehouses and the EDW.
- Reports can be specific to departmental needs or organization-wide, providing actionable insights based on historical data.
-
Dashboards:
- Visual interfaces that display key performance indicators (KPIs) and metrics in an easily digestible format.
- Dashboards pull data from the EDW and provide real-time insights to business users.
-
Alerts:
- Notifications triggered by specific events or thresholds defined in the data.
- Alerts help users to take timely actions based on critical data points.
-
Data Science Users:
- These are analysts, data scientists, and other professionals who utilize data for advanced analytics, machine learning, and statistical modeling.
- They interact with the data stored in the EDW and department warehouses to conduct in-depth analyses and derive predictive insights.
Flow of Data
-
Data Collection:
- Data from various sources flows into the system, being first collected and processed either directly into the Department Warehouse or the Enterprise Data Warehouse (EDW).
-
Storage and Management:
- Department-specific data is stored in the Department Warehouse, while organization-wide data is consolidated in the EDW.
- The EDW acts as the central hub, integrating data from different departments and sources.
-
Data Utilization:
- Reports are generated from both the Department Warehouse and EDW to meet specific and general analytical needs.
- Dashboards pull data from the EDW to present real-time insights.
- Alerts are set up based on the data in the EDW to notify users of critical events or anomalies.
-
End-User Interaction:
- Data Science Users access the EDW for comprehensive data analysis, applying advanced analytical techniques to extract deeper insights.
- Business users interact with dashboards and reports for decision-making.
Importance of Each Component
- Different Data Sources: Ensures that all relevant data, regardless of origin, is captured for analysis.
- Department Warehouse: Provides tailored data storage and reporting capabilities for specific departmental needs.
- Enterprise Data Warehouse (EDW): Offers a unified view of the organization’s data, supporting cross-departmental analytics and comprehensive data management.
- Reports: Provide historical insights and support business decision-making based on data.
- Dashboards: Offer real-time visualization of key metrics, enhancing the ability to monitor and respond to changes quickly.
- Alerts: Enable proactive management by notifying users of critical events or changes in data patterns.
- Data Science Users: Play a crucial role in extracting advanced insights, applying predictive and prescriptive analytics to drive strategic initiatives.
This architecture ensures a seamless flow of data from collection to actionable insights, supporting both operational and strategic needs within the organization.