Learning Vector Quantisation
Definition
Learning Vector Quantisation (LVQ) is a supervised learning algorithm that uses prototype vectors to classify input data into predefined categories. It is based on competitive learning, where the prototypes (representing different classes) are updated during training to better represent the underlying data distribution.
Key Concepts
- Prototype Vectors: Representative vectors for each class that are adjusted during training.
- Supervised LearningSupervised LearningSupervised Learning Definition Supervised Learning is a type of machine learning where the algorithm is trained on a labeled dataset. Each training example consists of an input object (typically a vector) and a desired output value (also called the supervisory signal). The goal is for the model to learn to map inputs to outputs so it can predict the output of new, unseen data. Key Concepts Labeled Data:** Data that includes both input features and the corresponding correct output. Training a: LVQ uses labeled input data to learn the classification boundaries.
- Competitive Learning: The prototype closest to the input vector is identified and updated.
- [Quantisation]: The process of mapping input vectors to the nearest prototype, which determines the class assignment.
Detailed Explanation
Prototype Vectors
- Initialization: Prototypes are initialized, typically with small random values or samples from the training data.
- Representation: Each prototype represents a specific class and is updated to better capture the characteristics of that class.
Supervised Learning
- Labeled Data: LVQ requires labeled training data to learn the classification boundaries between different classes.
- Training Process:
- Input Vector Presentation: An input vector from the training dataset is presented.
- Finding the Best Matching Unit (BMU): The prototype closest to the input vector (measured by Euclidean distance) is identified as the BMU.
- Updating Prototypes: The BMU is updated to move closer to or further from the input vector, depending on whether the BMU correctly or incorrectly classifies the input vector.
Competitive Learning
- BMU Identification: For each input vector, the prototype with the smallest Euclidean distance to the input vector is selected as the BMU.
- Update Rule: [ \mathbf{w}_i(t+1) = \mathbf{w}_i(t) + \alpha(t) (\mathbf{x} - \mathbf{w}_i(t)) ] where ( \mathbf{w}_i(t) ) is the weight vector of the BMU at time ( t ), ( \alpha(t) ) is the learning rate, and ( \mathbf{x} ) is the input vector.
Quantization
- Mapping Input Vectors: During the classification phase, input vectors are mapped to the nearest prototype vector, which determines their class.
- Decision Boundaries: The locations of the prototype vectors determine the decision boundaries between different classes.
Diagrams
Basic Structure of Learning Vector Quantization
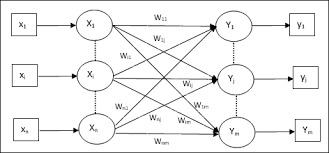
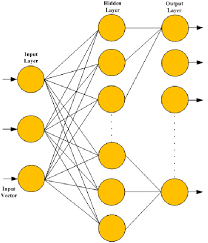
LVQ Training Process
Links to Resources
- Learning Vector Quantization Overview: Detailed reference entry on LVQ, explaining its principles and applications.
- Introduction to Learning Vector Quantization: An accessible introduction to LVQ with examples and practical insights.
- Neural Networks and Learning Machines by Simon Haykin: Textbook providing in-depth coverage of LVQ and other neural network models.
Notes and Annotations
- Summary of Key Points:
- LVQ is a supervised learning algorithm that uses prototype vectors to classify data.
- Prototypes are adjusted based on labeled training data to better represent class boundaries.
- The algorithm uses competitive learning to update the prototype closest to each input vector.
- Input vectors are mapped to the nearest prototype, determining their class assignment.
- Personal Annotations and Insights:
- LVQ is particularly useful for problems where the decision boundaries between classes are complex and non-linear.
- The interpretability of LVQ models, due to the explicit representation of prototypes, can be advantageous in understanding the classification process.
Backlinks
- Self-Organizing Maps (SOM) Algorithm: Refer to notes on the SOM algorithm for a related unsupervised learning technique that also uses competitive learning.
- Adaptive Resonance Theory (ART) Networks: Connect to notes on ART networks to see another approach to maintaining stability and plasticity in learning.
- Neural Network Models Overview: Link to an overview of different neural network models to see where LVQ fits in the landscape of machine learning techniques.