Definition of Virtualization
Definition
Virtualisation in cloud computing is a technology that allows the creation of multiple simulated environments or dedicated resources from a single, physical hardware system. It enables the abstraction and partitioning of a physical machine into multiple virtual machines (VMs), each running its own operating system and applications as if it were a separate physical device.
Key Concepts
- hypervisorhypervisorBacklinking * Virtualization Architecture and Software * Definition of Virtualization * Define virtualizations? Explain the advantages and disadvantages of Virtualization?: Software that creates and manages virtual machines by providing a virtual operating platform to each VM.
- Virtual Machine (VM)Images: An emulation of a computer system that runs on a hypervisorhypervisorBacklinking * Virtualization Architecture and Software * Definition of Virtualization * Define virtualizations? Explain the advantages and disadvantages of Virtualization?, allowing multiple operating systems to run on a single physical machine.
- Host MachineImages: The physical hardware system that runs the hypervisor and hosts multiple VMs.
- Guest Machine: The virtual machines that run on the host machine.
- VMware, KVM, Hyper-V: Popular hypervisors used for virtualization.
- Resource Allocation: The process of distributing hardware resources (CPU, memory, storage) among multiple VMs.
- IsolationIsolationSecurity* and Stability: **Hypervisors isolate VMs from each other, preventing one VM from affecting the others. This isolation is crucial for maintaining security and stability, especially in multi-tenant cloud environments (Vittana). Fault Tolerance**: By isolating VMs, hypervisors help in maintaining system integrity. If one VM crashes, it does not impact the operation of other VMs on the same host (Startuptalky).: Ensuring that each VM operates independently without interference from others.
Detailed Explanation
Virtualisation enables better utilisation of physical hardware by allowing multiple virtual environments to run on a single physical machine. This results in more efficient use of resources, reduced costs, and increased flexibility in managing computing environments.
-
HypervisorsHypervisorsType 1 Hypervisors: These are installed directly on the **physical server hardware**, without needing **a host operating system**. They **provide better performance and lower latency compared to Type 2 hypervisors**. Examples include ***VMware ESXi, Microsoft Hyper-V, and Xen. Type 2 Hypervisors*: These run on a **host operating system that provides hardware abstraction and other services. They are easier to set up and are commonly used for desktop virtualization. Examples include VMware Worksta: Hypervisors can be classified into two types:
- Type 1 (Bare-Metal)Type 1 (Bare-Metal)These hypervisors run directly on the physical hardware, providing better performance and efficiency. Examples include VMware ESXi and Microsoft Hyper-V.: These hypervisors run directly on the physical hardware, providing better performance and efficiency. Examples include VMware ESXi and Microsoft Hyper-V.
- Type 2 (Hosted)Type 2 (Hosted)These hypervisors run on top of an existing operating system, making them easier to set up but generally less efficient. Examples include VMware Workstation and Oracle VirtualBox.: These hypervisors run on top of an existing operating system, making them easier to set up but generally less efficient. Examples include VMware Workstation and Oracle VirtualBox.
-
VM Lifecycle Management: Virtualisation allows for easy creation, deployment, migration, and deletion of VMs, simplifying infrastructure management and scaling.
-
Resource Allocation and Management: Virtualisation technologies provide mechanisms for dynamically allocating resources such as CPU, memory, and storage to VMs based on demand, ensuring optimal performance and utilization.
-
IsolationIsolationSecurity* and Stability: **Hypervisors isolate VMs from each other, preventing one VM from affecting the others. This isolation is crucial for maintaining security and stability, especially in multi-tenant cloud environments (Vittana). Fault Tolerance**: By isolating VMs, hypervisors help in maintaining system integrity. If one VM crashes, it does not impact the operation of other VMs on the same host (Startuptalky). and Security: Each VM is isolated from others, enhancing security by preventing one VM from accessing the data or resources of another. This isolation also helps in fault tolerance, as issues in one VM do not affect others.
-
Snapshots and Cloning: Virtualisation platforms support taking snapshots of VMs, which capture the state of a VM at a particular point in time, and cloning, which creates an exact copy of a VM. These features are crucial for backup, recovery, and rapid deployment.
Diagrams
Diagram 1: Basic Virtualisation Architecture
- A simple diagram showing a physical server (host machine) with a hypervisor running multiple VMs.
Diagram 2: Hypervisor Types
- A comparison of Type 1 and Type 2 hypervisors with examples.
Diagram 3: Resource Allocation
- Visualisation of how CPU, memory, and storage are allocated to different VMs from the host machine.
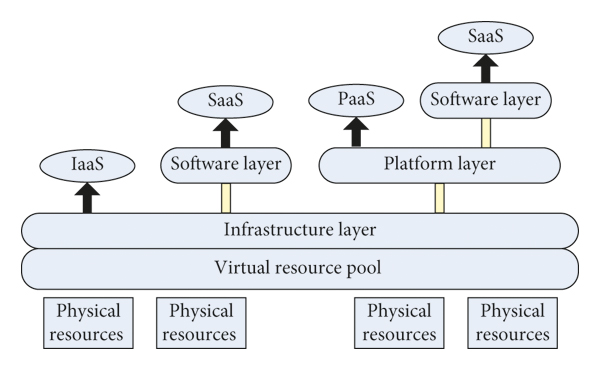
Links to Resources
- IBM Virtualisation - IBM
- Understanding Hypervisors - Microsoft Docs
- Virtualization Concepts - Red Hat
- Introduction to Virtualization - VMware
- KVM Virtualization - Linux KVM
Notes and Annotations
- Summary of Key Points: Virtualization abstracts physical hardware to create multiple virtual environments, enhancing resource utilization, security, and management flexibility.
- Personal Annotations and Insights: Virtualization is fundamental to cloud computing, as it enables the on-demand provision of computing resources and services, forming the backbone of Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) offerings.
Backlinks
- Cloud Computing Basics: Understanding how virtualization integrates into broader cloud infrastructure.
- Resource ManagementResource ManagementEfficient Utilisation*: Hypervisors enable **better utilization of physical resources by allowing multiple VMs to share the same hardware, thus reducing wastage and improving efficiency. Dynamic Allocation*: They can dynamically allocate resources such as **CPU, memory, and storage based on the needs of individual VMs, ensuring optimal performance and resource distribution.: Techniques and best practices in allocating resources in virtualized environments.
- Security in Cloud Computing: How virtualization enhances isolation and security within cloud ecosystems.
- Types of VirtualizationTypes of VirtualizationDefinition Virtualization in cloud computing involves creating virtual versions of physical resources, such as servers, storage devices, networks, and even entire operating systems. This abstraction allows multiple virtual resources to run on a single physical resource, enhancing efficiency, flexibility, and scalability. Key Concepts Server Virtualization**: Creating multiple virtual servers from a single physical server. Storage Virtualization*: Combining multiple physical storage devices in
- Virtual InfrastructuresVirtual InfrastructuresDefinition Virtual infrastructure refers to the virtualized environment that includes virtual machines (VMs), virtual networks, virtual storage, and the management tools that support them. It abstracts and pools physical resources, enabling the creation of flexible, scalable, and efficient IT environments. Key Concepts Virtual Machines (VMs)**: Emulated computer systems that run an operating system and applications. Hypervisors**: Software that creates and manages VMs by providing a virtual o
- Virtualization Architecture and SoftwareVirtualization Architecture and SoftwareDefinition Virtualization architecture refers to the framework and components that enable the creation, management, and operation of virtual environments. Virtualization software includes hypervisors and management tools that facilitate the deployment and control of virtual machines (VMs) and other virtual resources. Key Concepts hypervisor: The **core software that enables virtualization by allowing multiple operating systems to run concurrently on a host machine. Type 1 Hypervisor (Bare-Met
- CPU, Network, and Storage VirtualizationCPU, Network, and Storage VirtualizationDefinition CPU, network, and storage virtualization refer to the technologies and processes used to abstract and pool physical computing resources, enabling their flexible and efficient use within virtualized environments. These types of virtualization are essential for creating scalable, flexible, and efficient cloud infrastructure. Key Concepts CPU Virtualization**: Abstracting the physical CPU to create multiple virtual CPUs (vCPUs) that can be allocated to virtual machines (VMs). Network
- Define virtualizations? Explain the advantages and disadvantages of Virtualization?