Computer Simulations
Definition
Computer simulations are the use of computational models to replicate and study the behavior of complex systems and processes. These simulations allow researchers and practitioners to analyze, predict, and visualize outcomes without the need for physical experimentation, saving time and resources while providing deeper insights into the systems being studied.
Key Concepts
- Modelling: The process of creating a mathematical representation of a real-world system.
- Simulation: The execution of a model to study its behavior over time.
- Validation and Verification: Ensuring that the simulation accurately represents the real-world system and behaves as expected.
- Visualisation: The graphical representation of simulation results to facilitate understanding and analysis.
Detailed Explanation
Modeling
- System Representation: Creating a mathematical or logical model that represents the key characteristics and behaviors of the system.
- Types of Models: Models can be deterministic or stochastic, continuous or discrete, depending on the nature of the system and the desired analysis.
Simulation
- Execution: Running the model on a computer to simulate the behavior of the system over time.
- Time Steps: Simulations often proceed in discrete time steps, where the state of the system is updated incrementally.
- Parameters and Inputs: Simulations require inputs and parameters that define the initial conditions and rules governing the system's behavior.
Validation and Verification
- Validation: Ensuring that the model accurately represents the real-world system by comparing simulation results with real data.
- Verification: Ensuring that the simulation code correctly implements the model and is free of errors.
Visualisation
- Graphical Representation: Using charts, graphs, animations, and other visual tools to represent simulation results.
- Analysis: Visualization aids in understanding complex behaviors, identifying patterns, and communicating findings effectively.
Diagrams
Example of a Simulation Process Flow
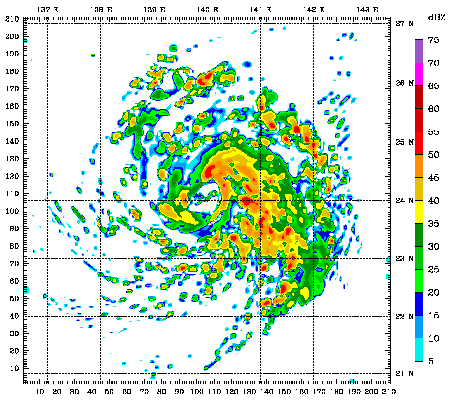
Example of Simulation Results Visualization
Links to Resources
- Introduction to Computer Simulation: A comprehensive guide to the principles and practices of computer simulation.
- Simulation Modeling and Analysis by Averill M. Law: A widely used textbook on simulation modeling and analysis techniques.
- AnyLogic Simulation Software: A leading simulation software tool that supports various types of simulations including discrete event, agent-based, and system dynamics.
Notes and Annotations
- Summary of Key Points:
- Computer simulations involve creating and running models to study complex systems.
- Key aspects include modeling, simulation execution, validation and verification, and visualization of results.
- Simulations are powerful tools for analyzing, predicting, and visualizing system behaviors without physical experimentation.
- Personal Annotations and Insights:
- The ability to simulate complex systems allows for experimentation with different scenarios, providing valuable insights into potential outcomes and aiding in decision-making.
- Visualization of simulation results is crucial for effectively communicating findings and facilitating a deeper understanding of the system's behavior.
Backlinks
- Self-Organizing Maps (SOM) Algorithm: Refer to notes on the SOM algorithm for an example of how computer simulations can be used to study and visualize the behavior of neural networks.
- Adaptive Resonance Theory (ART) Networks: Connect to notes on ART networks to see how simulations can be used to validate and understand these models.
- Unsupervised Learning Techniques: Link to discussions on various unsupervised learning methods and their applications, many of which rely on computer simulations for analysis and validation.