Components of Competitive Learning (CL) Network
Definition
Competitive Learning (CL) Network is a type of artificial neural network where neurons compete to become active during the learning process. Only the neuron with the highest activation (winner) is updated, reinforcing its weight vectors to match the input pattern. This learning strategy is primarily used for tasks like clustering, pattern recognition, and vector quantisation.
Key Concepts
- Competition: Neurons in the network compete to be the one to respond to a given input.
- Winner-Take-All: The neuron with the highest activation is the only one that updates its weights.
- Weight Update Rule: The winning neuron's weights are adjusted to be closer to the input vector.
- Normalisation: Weights are often normalised to maintain stability and ensure meaningful competition.
Detailed Explanation
- Competition Mechanism: In a CL network, when an input is presented, each neuron computes its activation based on a similarity measure (often a dot product between the input vector and the neuron's weight vector). The neuron with the highest activation "wins" the competition.
- Winner-Take-All Strategy: Only the weights of the winning neuron are updated. This strategy ensures that neurons become specialised in responding to different regions of the input space.
- Weight Update Rule: The winning neuron's weights are updated using the following rule: [$$ \mathbf{w}_i(t+1) = \mathbf{w}_i(t) + \eta (\mathbf{x} - \mathbf{w}_i(t)) $$] where ( \mathbf{w}_i(t) ) is the weight vector of the winning neuron at time ( t ), ( \eta ) is the learning rate, and ( \mathbf{x} ) is the input vector.
- Normalisation: To prevent the weights from growing unbounded, they are often normalised after each update: [$$ \mathbf{w}_i(t+1) = \frac{\mathbf{w}_i(t+1)}{|\mathbf{w}_i(t+1)|} $$]
Diagrams
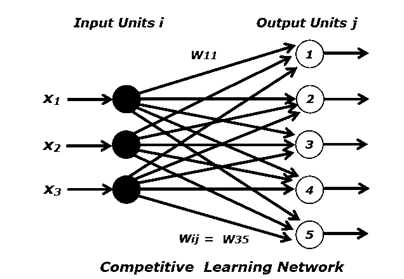
Components of a Competitive Learning Network:
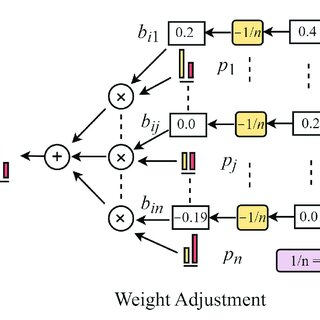
Example of Weight Adjustment:
Links to Resources
- Understanding Competitive Learning Networks: A comprehensive research paper on the fundamentals and applications of competitive learning networks.
- Neural Networks and Learning Machines by Simon Haykin: A textbook providing detailed coverage on competitive learning networks and other neural network paradigms.
- Kohonen's Self-Organizing Maps (SOM): An in-depth resource on a specific type of competitive learning network developed by Teuvo Kohonen.
- Introduction to Competitive Learning Networks - Academic Paper
- Fundamentals of Neural Networks - Book
- Competitive Learning and Kohonen Maps
Notes and Annotations
- Summary of Key Points:
- Competitive Learning (CL) involves neurons competing to respond to input patterns.
- Only the neuron with the highest activation updates its weights (winner-take-all).
- Weight normalization is crucial for stability.
- Personal Annotations and Insights:
- CL networks are particularly effective for unsupervised learning tasks such as clustering and vector quantisation.
- The normalisation step ensures that neurons develop distinct specializations, enhancing the network's ability to differentiate between input patterns.
Backlinks
- Competitive Learning Neural Networks
- Introduction to Artificial Neural Networks
- Learning Algorithms
- Artificial Neural Networks (ANN) Overview
- Self-Organizing Maps (SOM)
- Unsupervised Learning Techniques