Building Blocks of CNNs
Definition
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) are a class of deep neural networks commonly used in analyzing visual imagery. They are designed to automatically and adaptively learn spatial hierarchies of features from input images. CNNs are widely used in image and video recognition, recommender systems, image classification, medical image analysis, and more.
Key Concepts
- Convolutional Layer
- Activation Function (ReLU)
- Pooling Layer
- Fully Connected Layer
- Dropout
- Batch Normalization
Detailed Explanation
Convolutional Layer
- Purpose: Detects local patterns in the input image by applying convolution operations using filters or kernels.
- Mechanism: A filter (small matrix of weights) slides over the input image to produce feature maps. Each filter captures different features like edges, textures, etc.
- Parameters: Kernel size, stride, padding, and the number of filters.
Activation Function (ReLU)
- Purpose: Introduces non-linearity to the model, allowing it to learn more complex patterns.
- Mechanism: Applies the Rectified Linear Unit (ReLU) function, which sets all negative values to zero and keeps positive values unchanged.
- Formula: ( f(x) = \max(0, x) )
Pooling Layer
- Purpose: Reduces the spatial dimensions of the feature maps, decreasing the computational load and preventing overfitting.
- Types: Max pooling (most common), average pooling.
- Mechanism: Aggregates values (e.g., taking the maximum or average) within a sliding window across the feature map.
Fully Connected Layer
- Purpose: Acts as a traditional neural network layer, connecting every neuron in one layer to every neuron in the next layer.
- Mechanism: Flattens the input and applies weights and biases to generate the final output, often for classification.
Dropout
- Purpose: Prevents overfitting by randomly setting a fraction of input units to zero during training.
- Mechanism: Each neuron is kept with a probability p and set to zero with probability 1-p during each forward pass.
Batch Normalization
- Purpose: Stabilizes and accelerates the training process by normalizing the inputs of each layer.
- Mechanism: Normalizes the activations of the previous layer for each mini-batch, ensuring a stable distribution of inputs.
Diagrams
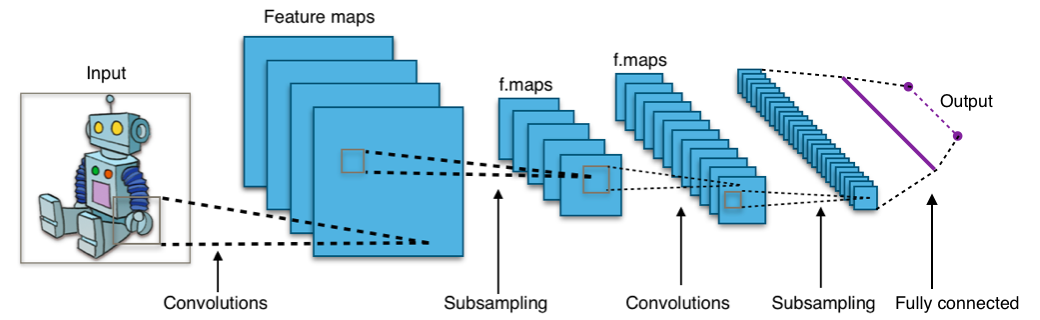
- Convolutional Layer: Visual representation of filters applied to input image, resulting in feature maps.
- ReLU Activation: Graph of ReLU function.
- Pooling Layer: Example of max pooling operation.
- Fully Connected Layer: Illustration of dense connections between layers.
- Dropout: Diagram showing randomly omitted neurons during training.
- Batch Normalization: Depiction of normalization across a mini-batch.
Links to Resources
- Stanford CS231n: Convolutional Neural Networks for Visual Recognition
- Deep Learning Book by Ian Goodfellow: Convolutional Networks
- PyTorch Tutorials: Deep Learning with PyTorch: A 60 Minute Blitz
- TensorFlow Guide: Convolutional Neural Networks
Notes and Annotations
Summary of Key Points
- CNNs are specifically designed for image analysis tasks.
- Convolutional layers detect local features using filters.
- ReLU introduces non-linearity, essential for learning complex patterns.
- Pooling layers reduce spatial dimensions and computational load.
- Fully connected layers interpret the high-level features for classification.
- Dropout prevents overfitting by randomly deactivating neurons during training.
- Batch normalization stabilizes learning by normalizing layer inputs.
Personal Annotations and Insights
- When choosing kernel sizes, smaller kernels (e.g., 3x3) are generally preferred as they capture fine details while preserving spatial information.
- The depth (number of filters) of convolutional layers increases with network depth to capture more abstract features.
- Dropout rates typically range from 0.2 to 0.5; higher rates may lead to underfitting.
- Batch normalization can also act as a regularizer, potentially reducing the need for dropout.
Backlinks
- Artificial Neural Networks: Detailed understanding of how CNNs fit within the broader category of ANNs.
- Deep Learning Algorithms: Exploration of other deep learning architectures and their applications.
- Image Processing: Practical applications of CNNs in preprocessing and analyzing visual data.